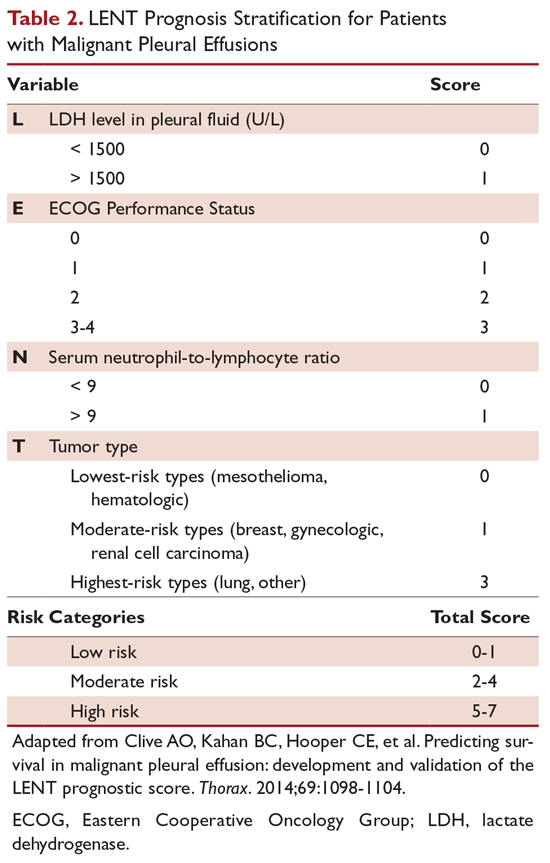
is malignant pleural effusion stage 4
Escape of a fluid into a part. Pleural effusion in other conditions R0689 Other abnormalities of breathing 11 5119 Unspecified pleural effusion J918 classified elsewhere 12 79380 Unspecified abnormal mammogram R928 Other abnormal and inconclusive findings on diagnostic imaging of breast 13 7840 Headache R51 Headache Other nonspecific abnormal finding of.
Medicina Free Full Text Malignant Pleural Effusion And Its Current Management A Review Html
Staging is an important part of.
. Malignant pleural effusions can worsen some of. A person can develop a pleural effusion in the absence of pleurisy. Stage IA2 T1b N0 M0.
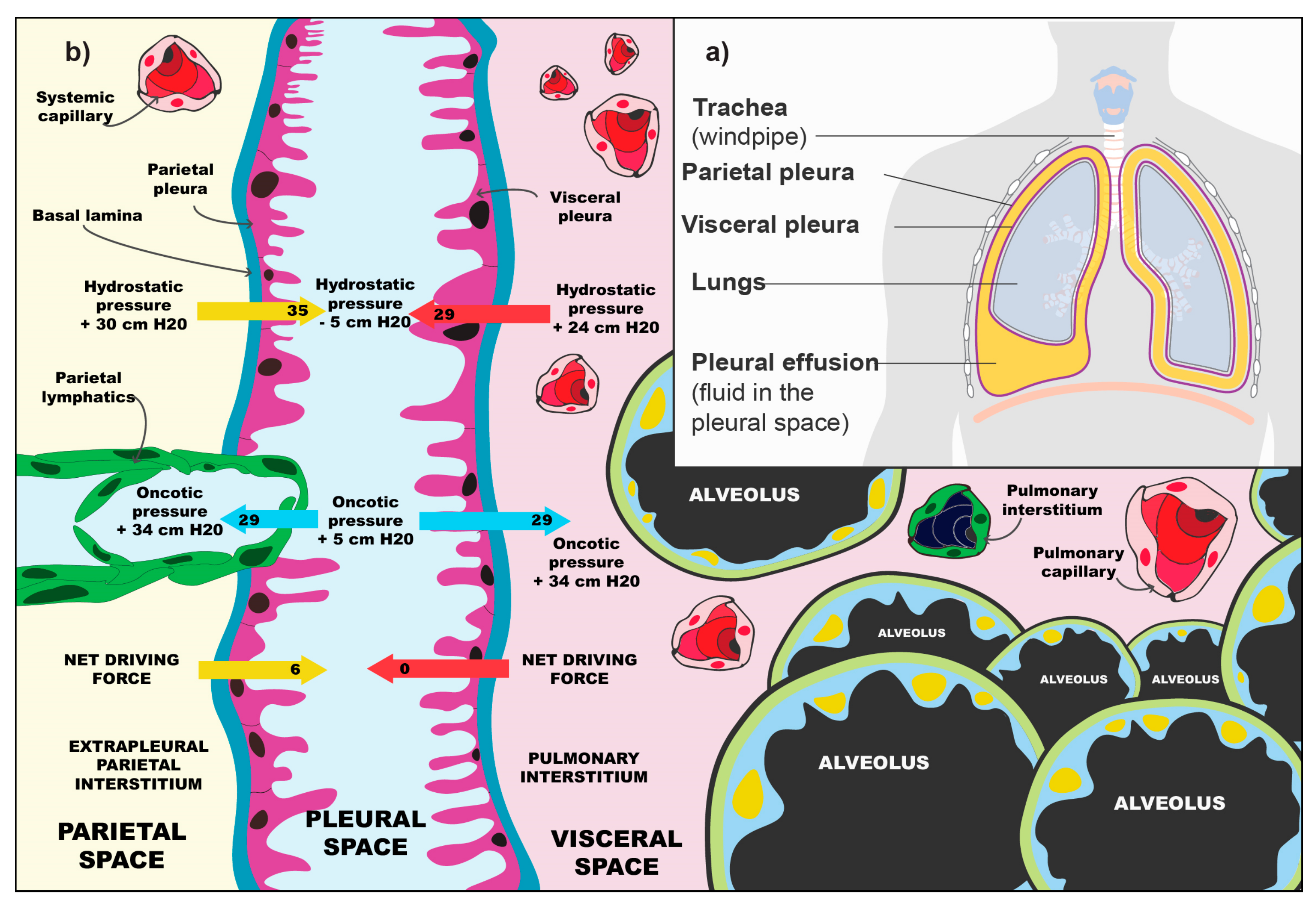
A pleural effusion is an abnormal fluid buildup between the pleural layers. The depth of the effusion can be used to estimate the likely volume of fluid provided the fluid is relatively evenly spread throughout the pericardium ie. This occurs in about 30 percent of lung cancers but can also occur with other cancers such as breast cancer ovarian cancer leukemia and lymphoma.
The modern SVAD provides reliable access for blood withdrawal and medication administration with minimal disruption to a patients lifestyle. Less common than lung cancer mesothelioma is a. Most malignant pleural effusions cause symptoms and the spatial extent of pleural effusions is correlated with the probability of malignant disease ie the larger a unilateral effusion is the more likely that cancer is the cause.
Clearly this does not apply to loculated effusions. It is called an exudate if it escapes exudes into the pleural cavity. Stage IVB Any T Any N M1 TNM-8 Oesphagogastric Junction.
Sargent reported using a 9 F catheter to treat pneumothoraces in 1970. Lung cancer is the most common cause accounting for more than one-third of cases followed by breast cancer 168 and malignant. Pericardial effusion the accumulation of an abnormally large amount of pericardial fluid in the pericardium.
4 Robinson applied Tenckhoff catheters for palliative drainage of malignant pleural effusion in nine patients. For example pneumonia heart failure cancer or a pulmonary embolism can lead to a pleural effusion. Malignant pleural effusion MPE is the terminal stage of cancer and the current standard of care for MPE is largely palliative.
Pleural effusion involving fibrinous exudates in the fluid may be called fibrinous pleurisy which sometimes occurs as a later stage of pleurisy. 3 Lawless and colleagues from the University of Pittsburgh used an 85 F pigtail catheter for the treatment of pneumothorax in 16 neonates and small children with a high success rate. It is often difficult to manage in end.
Chyliform effusion see chylothorax. Chylous effusion see chylothorax. An exudate or transudate.
Findings from the physical exam such as dullness to percussion of the lung area when. Hydrothorax is a type of pleural effusion in which transudate accumulates in the pleural cavityThis condition is most likely to develop secondary to congestive heart failure following an increase in hydrostatic pressure within the lungsMore rarely hydrothorax can develop in 10 of patients with ascites which is called hepatic hydrothorax. The stages of mesothelioma range from 1 to 4 and are based on tumor size and location.
Pleural effusion cancer life expectancy - Malignant pleural effusion is a complication involving the accumulation of fluid containing cancer cells between the membranes covering the lungs. M1c Multiple extrathoracic metastasis in a single or multiple organs. This buildup can cause chest pain especially when breathing deeply shortness of breath and coughing.
Tumour with pleural or pericardial nodules or malignant pleural or pericardial effusion. Early-stage mesothelioma is more confined to one site while late-stage mesothelioma shows tumors spreading beyond the chest or abdominal cavity. For example a patient with a history of congestive heart failure or cirrhosis with symptoms of cough difficulty breathing and pleuritic chest pain may have a pleural effusion.
Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity between the lining of the lungs and the thoracic cavity ie the visceral and parietal pleuraeThe pleural fluid is called a transudate if it permeates transudes into the pleural cavity through the walls of intact pulmonary vessels. This can cause a build-up of excess fluid a condition known as a malignant pleural effusion. Here the authors design a liposomal nanoparticle loaded with cyclic.
In a contralateral lobe. M1b Single extrathoracic metastasis in a single organ. Stage IA T1 N0 M0 Stage IA1 T1miT1a N0 M0.
The patients history and physical exam may indicate a presumptive diagnose of pleural effusion. Because of improved materials and. The subcutaneous venous access device SVAD or port is a critical component in the care of patients with chronic disease.
Air or gas also can build up in the pleural space. Accumulated fluid from a pericardial effusion evacuated by the. Other potential symptoms of pleural tumors include general discomfort fatigue and unintended weight loss.
Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key

Overall Survival Probability According To Malignant Pleural Effusion Download Scientific Diagram

Malignant Pleural Effusions Thoracic Key
Malignant Pleural Effusion Still A Long Way To Go Researcher An App For Academics

Malignant Pleural Effusion Management Keeping The Flood Gates Shut The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Stage 4 Mesothelioma Prognosis Treatment Life Expectancy

Treatment Options For Malignant Pleural Effusions Download Table

The Diagnostic Steps In Suspected Malignant Pleural Effusion Table 1 Download Scientific Diagram
Malignant Pleural Effusion Evaluation And Diagnosis Pulmonary Health Hub